Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology*
JAEA-Review 2022-051, 78 Pages, 2023/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Establishing a new evaluation system to characterize radiation carcinogenesis by stem cell dynamics" conducted from FY2019 to FY2021. Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for three fiscal years were summarized. In this study, we will use cell lineage tracing technology that can permanently label stem cells and their progenies to capture and mathematically model the long-term clonal proliferation of cells in mammary tissue after high to low dose radiation exposure to determine the origin of radiation carcinogenesis, the stem cells. The objective is to characterize radiation-induced breast cancer by its dynamics.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology*
JAEA-Review 2021-052, 52 Pages, 2022/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Establishing a new evaluation system to characterize radiation carcinogenesis by stem cell dynamics" conducted in FY2020. In this study, the long-term clonal expansion of mammary stem cells after high- to low-dose radiation exposure was investigated using stem-cell lineage tracing technology that can permanently label stem cells and their progenies. The purpose of this study is to characterize radiation-induced breast cancer based on the dynamics of radiation-exposed stem cells by capturing proliferation and analyzing it using a mathematical model.
Ichihara, Yoshitaka*; Nakamura, Naohiro*; Moritani, Hiroshi*; Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi
Frontiers in Built Environment (Internet), 7, p.676408_1 - 676408_14, 2021/06
The objective of this study is the improvement of response evaluations of structures, facilities and equipment in evaluation of three-dimensional seismic behavior of nuclear power plant facilities, by three-dimensional finite element method model, including separation and sliding between the soil and the basement walls. To achieve this, simulation analyses of Kashiwazaki Kariwa nuclear power plant unit 7 reactor building under the 2007 Niigataken-chuetsu-oki earthquake event were carried out. These simulation analyses consider soil-structure interaction using a three-dimensional finite element method model in which the soil and building are three-dimensionally modeled by the finite element method. It is found that basemat uplift is generated on east side of the basemat edge, and this has an important influence on the results. The importance is evidenced by the difference of local response in soil pressure characteristics beneath the edge of basemat, the soil pressure characteristics along the east side of basement wall and the maximum acceleration response at the west end of the embedded surface. Although, in this particular study, basemat uplift, separation and sliding have only a relatively small influence on the maximum acceleration response of embedded surface and the soil pressure characteristics along the basement walls and beneath the basemat, under strong earthquake motion, these influences can be significant, therefore appropriate evaluation of this effect should be considered.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; National Institutes for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology*
JAEA-Review 2020-045, 52 Pages, 2021/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Establishing a new evaluation system to characterize radiation carcinogenesis by stem cell dynamics" conducted inFY2019. In this study, the long-term clonal expansion of mammary stem cells after high- to low-dose radiation exposure was investigated using stem-cell lineage tracing technology that can permanently label stem cells and their progenies. The purpose of this study is to characterize radiation-induced breast cancer based on the dynamics of radiation-exposed stem cells by capturing proliferation and analyzing it using a mathematical model. The goal of this study is to develop a new evaluation system that can characterize previously undiscovered "radiation signatures" by stem cell dynamics.
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Sato, Tatsuhiko
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.03015_1 - 03015_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.1(Nuclear Science & Technology)Particle transport simulation codes based on the Monte Carlo technique have been successfully applied to shielding calculations in accelerator facilities. Estimation of not only statistical uncertainties, which depend on the number of trials, but also systemic uncertainties, which are caused by uncertainty of total cross section models, is required to confirm the reliability of the simulation results. We evaluated unclear quantities of internal parameters included in the total cross section model by the KALMAN code, which is based on the least squares technique, comparing with experimental data of the total cross section. The uncertainties in the total cross sections obtained by the new model are comparable to the experimental errors. In the present study, the systematic uncertainty included in the simulation results can be estimated by performing the transport calculations with variation of the internal parameters within their unclear quantities.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2019-026, 51 Pages, 2020/01
JAEA/CLADS had been conducting the Center of World Intelligence Project for Nuclear Science/Technology and Human Resource Development (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2018. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Establishment of Measurement System for Radiation-dependent Mutation in Organ Tissue Cells Derived from Human iPS Cells". The purpose of the present study is to establish an experimental system to evaluate the difference in radiation-dependent mutation among tissues. In previous studies, unified evaluation of the difference in radiation-dependent mutation among tissues has been difficult because the mutation rate among tissues had been evaluated using cell lines taken from different individuals. Recent biotechnological innovation in stem cell field represented by iPS cells has become enable to induce differentiation of tissue cells from a single cell. In the present study, Tokyo Institute of Technology produce tissue cells in nervous, dermal, blood and circulatory systems by unifying these new technologies. Using these tissue cells, we measure the mutation rate for each tissue after the radiation exposure, and aim to establish an experimental system to evaluate the difference in mutation depending on tissues by constructing a mathematical model.
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(4), p.345 - 354, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:48.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)Particle transport simulations based on the Monte Carlo method have been applied to shielding calculations. Estimation of not only statistical uncertainty related to the number of trials but also systematic one induced by unclear physical quantities is required to confirm the reliability of calculated results. In this study, we applied a method based on analysis of variance to shielding calculations. We proposed random- and three-condition methods. The first one determines randomly the value of the unclear quantity, while the second one uses only three values: the default value, upper and lower limits. The systematic uncertainty can be estimated adequately by the random-condition method, though it needs the large computational cost. The three-condition method can provide almost the same estimate as the random-condition method when the effect of the variation is monotonic. We found criterion to confirm convergence of the systematic uncertainty as the number of trials increases.
 Am reactor activation measurements
Am reactor activation measurements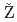 erovnik, G.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; Becker, B.*; Fiorito, L.*; Harada, Hideo; Kopecky, S.*; Radulovic, V.*; Sano, Tadafumi*
erovnik, G.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; Becker, B.*; Fiorito, L.*; Harada, Hideo; Kopecky, S.*; Radulovic, V.*; Sano, Tadafumi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 877, p.300 - 313, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:45.59(Instruments & Instrumentation)Methodologies to derive cross section data from spectrum integrated reaction rates were studied. The Westcott convention and some of its approximations were considered. The accuracy of the results strongly depends on the assumptions that are made about the neutron energy distribution, which is mostly parameterised as a sum of a thermal and an epi-thermal component. Resonance integrals derived from such data can be strongly biased. When the energy dependence of the cross section is known and information about the neutron energy distribution is available, a method to correct for a bias on the cross section at thermal energy is proposed. Reactor activation measurements to determine the thermal  Am(n,
Am(n,  ) cross section reported in the literature were reviewed, where the results were corrected to account for possible biases. These data combined with results of time-of-flight measurements give a capture cross section 720 (14) b for
) cross section reported in the literature were reviewed, where the results were corrected to account for possible biases. These data combined with results of time-of-flight measurements give a capture cross section 720 (14) b for  Am(n,
Am(n,  ) at thermal energy.
) at thermal energy.
Takeda, Toshikazu*; Yokoyama, Kenji; Sugino, Kazuteru
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 109, p.698 - 704, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.37(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new cross section adjustment method has been derived in which systematic errors in measured data and calculated results of neutronics characteristics are estimated and removed in the adjustment. Bias factors which are the ratio between measured data and calculated results are used to estimate systematic errors. The difference of the bias factors from unity is caused generally by systematic errors and stochastic errors. Therefore by determining whether the difference is within the total stochastic errors of measurements and calculations, systematic errors are estimated. Since stochastic errors are determined for individual confidence levels, systematic errors are also dependent to the confidence levels. The method has been applied to cross section adjustments using 589 measured data obtained from fast critical assemblies and fast reactors. The adjustments results are compared with those of the conventional adjustment method. Also the effect of the confidence level to the adjusted cross sections is discussed.
Furusawa, Akinori; Nishimura, Akihiko; Takebe, Toshihiko*; Nakamura, Masaki*; Takenaka, Yusuke*; Saijo, Shingo*; Nakamoto, Hiroyuki*
E-Journal of Advanced Maintenance (Internet), 9(2), p.44 - 51, 2017/08
The aim of this work is to investigate the applicability of ultrasonic guided wave for evaluation of laser beam butt-welding quality. Ten in total test pipes having welding seam is prepared. Two piece of pipe are jointed and continuous laser beam is irradiated on the edges, varying laser irradiation power, welding side and surface profile of the adjacent edges of the pipe. Ultrasonic guided wave testing experiment is performed on the pipes. Torsional mode guided wave is excited by EMAT. The experimental results are analyzed and issues are discussed. The reflection wave bullet from the poor interface of the welding seam is clearly observed, whereas no reflection from fine welded line. From the aspect of laser irradiation power, welding side and surface profile of the adjacent edges, the relation between the interface condition and detection wave bullet are analyzed. It is found that the ultrasonic guided wave technologies have the potential for evaluating laser beam butt-welding seam.
Kawaguchi, Kenji*; Maruyama, Yu; Zheng, X.
Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 56, p.153 - 195, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:54.4(Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence)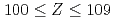 from alpha spectroscopy
from alpha spectroscopyAsai, Masato; He berger, F. P.*; Lopez-Martens, A.*
berger, F. P.*; Lopez-Martens, A.*
Nuclear Physics A, 944, p.308 - 332, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:95.62(Physics, Nuclear)Nuclear structure of Z = 100-109 nuclei studied through  -decay spectroscopy have been reviewed. Experimental techniques and methods concerning separation techniques, summing effects in
-decay spectroscopy have been reviewed. Experimental techniques and methods concerning separation techniques, summing effects in  spectra, and the use of digital electronics for
spectra, and the use of digital electronics for  -decay spectroscopy have been described in detail. The presentation of the experimental results and the physics discussion were focused on nuclear structure systematics in even-Z nuclei along the N = 151, 153, and 155 isotonic lines, where most progress has been achieved in the last 10 years.
-decay spectroscopy have been described in detail. The presentation of the experimental results and the physics discussion were focused on nuclear structure systematics in even-Z nuclei along the N = 151, 153, and 155 isotonic lines, where most progress has been achieved in the last 10 years.
Ouchi, Noriyuki
Hoken Butsuri, 40(2), p.166 - 169, 2005/06
Development of the new mathematical model of the carcinogenesis in a low dose in mind is reported. The new model which describes from cell canceration to the tumorigenesis in consideration of the physical dynamics of a cell level was built. In a cell group level, it has both intra-cellular dynamics, such as mutation, cell division, and cell death, and physical dynamics such as, adhesion between cells, modification, and movement, and a model can investigate with time that tumor is formed.
Matsunaga, Takeshi; Monte, L.; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Yanase, Nobuyuki; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Ueno, Takashi
JAERI-Review 2003-039, 150 Pages, 2004/01
Concerning radionuclides that might be released in an event of an accident from a nuclear facility, much attention has been paid to the migration pathways including the inflow to surface water bodies since the Chernobyl accident. In order to have discussions related to the current development of a mathematical model of the behavior of radionuclides in a river watershed, JAERI invited a guest scientist specializing in mathematical modeling of radioecology, Luigi Monte of Italian National Agency for New Technologies Energy and the Environment (ENEA: Ente per le Nuove tecnologie,L'Energia e l'Ambiente) of Italy, from May 22 to June 20 of 2003. This report is a summary of presentations and discussion made at the occasion of the visit of Dr. Monte at JAERI and also at relevant institutions of Japan involved in this study field. As a result of these discussions, distinct advantages and key problems of a mathematical model for prediction of the migration of radionuclides in a river watershed have been identified and analyzed.
Mineo, Hideaki; Goto, Minoru; Iizuka, Masaru*; Fujisaki, Susumu; Hagiya, Hiromichi*; Uchiyama, Gunzo
Separation Science and Technology, 38(9), p.1981 - 2001, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:63.65(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Katakura, Junichi
JAERI-Research 2003-004, 19 Pages, 2003/03
no abstracts in English
Endo, Akira; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Takahashi, Fumiaki
Radiation Risk Assessment Workshop Proceedings, p.151 - 156, 2003/00
We have developed a new system using numerical simulation technique for analyzing dose distribution in various postures by neutron, photon and electron exposures. The system consists of mathematical human phantoms with movable arms and legs and Monte Carlo codes MCNP and MCNPX. This system was applied to the analysis of dose distribution for the heavily exposed workers in the Tokai-mura criticality accident. The paper describes the simulation technique employed and a summary of the dose analysis.
Nagano, Tetsushi; Isobe, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Satoru*; Ashizaki, Midori*
Applied Spectroscopy, 56(5), p.651 - 657, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:50.32(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Mineo, Hideaki; Goto, Minoru; Iizuka, Masaru*; Fujisaki, Susumu; Uchiyama, Gunzo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(3), p.241 - 247, 2002/03
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:82.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Hwang, G.; Onuki, Kaoru
Journal of Membrane Science, 194(2), p.207 - 215, 2001/12
Times Cited Count:59 Percentile:87.26(Engineering, Chemical)no abstracts in English